How Maritime Insurance and PI Clubs Protect Ship Owners in 2026
- Dushyant Bisht

- Oct 2, 2025
- 9 min read
Updated: Jan 13

Picture this: A single container ship worth $200 million runs aground, blocking the Suez Canal for six days. The immediate damage? $9.6 billion in daily trade disruption. The Ever Given incident in 2021 was a stark reminder of how quickly billions can be lost when the unexpected happens at sea.
However, what most people don’t realize is that behind every ship navigating the world’s oceans is a sophisticated insurance ecosystem designed to protect against exactly these scenarios. P&I Clubs provide liability coverage for 90% of the world’s ocean-going tonnage, creating a safety net that enables global maritime trade, and maritime investment, to occur.
Whether you’re considering investing in shipping assets or want to understand how this $39.92 billion maritime insurance market protects the backbone of global commerce, this guide breaks down everything you need to know about naval risk management in 2026.
Why Maritime Insurance Matters
The numbers tell a compelling story. Only 27 ships over 100 GT were lost worldwide in 2024, representing a 20% drop from 35 in 2023 and a striking 75% decline from 105 losses reported a decade ago. This dramatic improvement is the result of stringent insurance requirements, advanced risk management, and comprehensive coverage systems.
Yet even with these improvements, the total number of marine casualties and incidents from 2014 to 2023 was 26,595, with an annual average of 2,660. Each incident represents potential financial exposure running into millions of dollars.
Consider the financial exposure: a modern container ship can cost over $200 million. In comparison, a specialized LNG carrier might reach over $300 million. Without proper insurance coverage, a single accident could wipe out entire investment portfolios. This is why marine insurance premiums reached $39.92 billion in 2024. The industry recognizes that prevention is far cheaper than loss.
Key Takeaway: Maritime insurance is the foundation that makes maritime investment economically viable by converting unpredictable catastrophic losses into predictable operating costs.
What Are P&I Clubs? (Protection & Indemnity Insurance Explained)

Protection & Indemnity (P&I) Clubs operate on a simple yet powerful principle: mutual insurance among shipowners. Unlike traditional commercial insurers focused on profit, P&I Clubs are non-profit mutual associations where members collectively share risks.
Here’s how it works: Ship owners pay annual premiums (called “calls”) based on their ship’s tonnage and risk profile. These funds create a collective pool used to cover third-party liability claims that any member might face. If claims exceed the pool, members may face supplementary calls for additional contributions.
The system has proven remarkably stable. Seven of the 12 major P&I clubs report combined ratios under 100%, with five being above 100%, indicating that most clubs operate profitably while providing comprehensive coverage.
The mutual advantage creates multiple benefits for both ship owners and ship operators. Clubs pool knowledge about maritime risks and best practices, sharing expertise across the global fleet. Cost efficiency arises from the non-profit structure, which eliminates commercial insurer profit margins and reduces costs for shipowners. Long—term stability results from a mutual structure that ensures a focus on member interests rather than shareholder returns. Global reach through International Group coverage provides worldwide protection across all major shipping routes.
From the Helm - Insider’s View: “The mutual insurance model works because every ship owner faces similar risks, weather, piracy, crew injuries, environmental damage. By pooling these risks, P&I Clubs can provide coverage that would be prohibitively expensive from commercial insurers. For maritime shipowners, this translates to predictable insurance costs and comprehensive protection that makes fractional ownership viable.”
The Risk Landscape: What Maritime Insurance Actually Covers

Maritime insurance operates across multiple layers, each addressing specific risk categories that could threaten vessel operations and investment returns.
Third-Party Liability Coverage
P&I insurance primarily covers liability to third parties, which can be massive. This includes collision damage when your vessel damages another ship, port infrastructure, or offshore installations. Cargo damage liability covers harm to cargo carried by your vessel or other ships. At the same time, personal injury claims encompass crew injuries, passenger accidents, or harm to people on different vessels. Wreck removal costs ensure funds are available to remove a sunken or damaged vessel from shipping lanes.
Environmental Protection
Environmental liability represents one of the largest potential exposures in modern shipping. Pollution cleanup encompasses oil spills, chemical releases, and other environmental contaminants that can cost hundreds of millions of dollars. Regulatory fines and penalties for violations can result in millions of dollars in additional costs. At the same time, third-party environmental claims encompass property damage and business interruption resulting from pollution incidents. The wreck removal environmental component prevents further environmental damage when vessels are lost or damaged.
Operational Liabilities
Day-to-day shipping operations create numerous liability exposures that P&I coverage addresses. Port state detention costs arise when vessels are detained for safety or regulatory violations, potentially incurring thousands of dollars in daily expenses. Crew repatriation ensures that crew members are returned home safely when vessels are detained or accidents occur. Legal defence coverage is crucial since maritime law is complex and legal costs can escalate quickly. General Average contributions apply when cargo is jettisoned to save the ship, requiring all parties to share the loss proportionally.
Beyond P&I: The Complete Maritime Insurance Ecosystem
While P&I coverage handles third-party liabilities, shipowners need additional coverage for first-party losses and specialised risks.
Hull & Machinery Insurance
This covers physical damage to the vessel itself across multiple scenarios. Total loss coverage applies if the vessel is destroyed or becomes a constructive total loss. In contrast, partial loss coverage handles repair costs resulting from damage caused by accidents, weather, or mechanical failure. Machinery breakdown coverage protects against expensive engine and equipment failures that can result in millions of dollars in repairs. Sue and labour costs cover emergency expenses incurred to prevent or minimise losses during maritime emergencies.
Loss of Hire Coverage
When a vessel can’t operate due to covered damage, Loss of Hire insurance provides critical financial protection. Daily hire compensation replaces lost charter revenue during repair periods, ensuring cash flow continues despite operational interruptions. Fixed cost coverage continues paying crew wages and other ongoing expenses that persist even when the vessel isn’t earning revenue. Port of refuge expenses cover additional costs when a damaged vessel must seek emergency repairs at the nearest suitable facility.
War Risks Insurance
Standard marine policies typically exclude war-related losses, requiring separate, specialised coverage. War, strikes, terrorism, and malicious damage (WSTM) coverage protects against political violence and terrorist attacks that standard policies won’t cover. Piracy and hijacking coverage has become increasingly important in certain trade routes where maritime criminal activity poses significant risks. Confiscation coverage protects against government seizure of vessels for political reasons. In contrast, blockade coverage applies when political events prevent vessel operations in specific regions.
Emerging Coverage: Cyber and ESG Risks
Modern maritime operations face new risks that require specialised coverage, which traditional policies often don’t address. Cyber liability coverage protects against hacking of navigation systems and ransomware attacks on port facilities that can cripple operations. Business interruption from cyber events covers lost revenue resulting from cyber attacks that disrupt vessel operations or port access. ESG compliance coverage addresses environmental, social, and governance violations that can result in significant fines and operational restrictions. Climate change adaptation coverage helps address extreme weather events and changing trade routes that create new operational challenges.
Real-World Impact: Case Studies in Maritime Risk Mitigation
Case Study 1: The Ever Given and Supply Chain Protection
When the Ever Given blocked the Suez Canal in March 2021, the immediate focus was on the $400 million in claims by the Suez Canal Authority. However, P&I coverage extended far beyond the vessel itself:
Third-party cargo claims: Delayed delivery of time-sensitive goods
Supply chain disruption: Business interruption for companies dependent on just-in-time delivery
Alternative routing costs: Additional fuel and port costs for hundreds of diverted vessels
The UK P&I Club’s coverage meant that individual cargo owners and supply chain participants had recourse for their losses, preventing a cascade of bankruptcies across global trade networks.
Case Study 2: Offshore Wind Farm Collision Protection
As offshore wind farms expand, shipping lanes also increase, leading to higher collision risks. Recent cases show how P&I coverage protects both ship owners and renewable energy infrastructure:
Infrastructure damage: Multi-million dollar wind turbine repairs
Environmental impact: Cable damage affecting power grid stability
Business interruption: Lost revenue for both shipping lines and energy producers
P&I coverage ensures that collision risks don’t prevent investment in either shipping or renewable energy infrastructure.
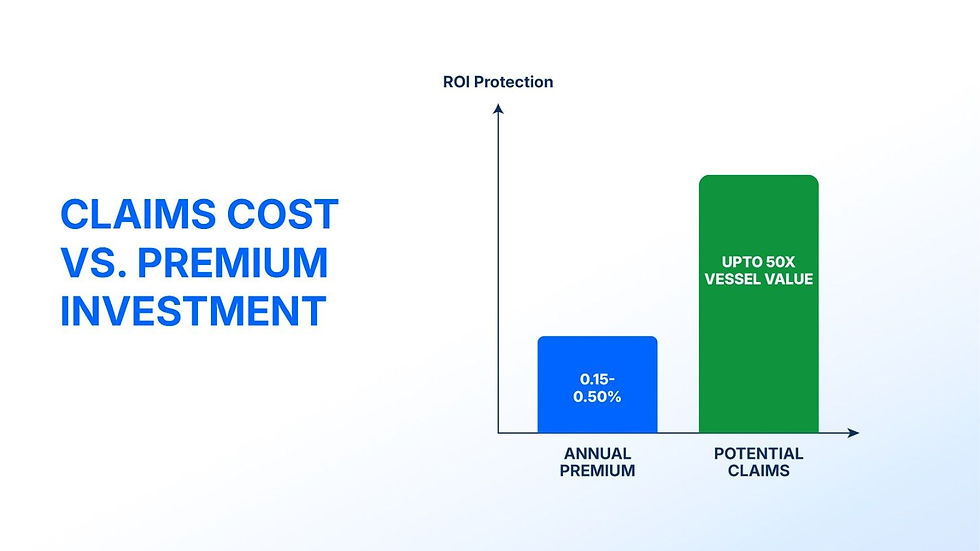
Cost-Benefit Analysis: Insurance as Investment Protection
For maritime shipowners, insurance costs represent a predictable expense that protects against unpredictable losses:
Typical insurance costs: 0.15% to 0.50% of vessel value annually for comprehensive coverage
Potential loss protection: Coverage limits often exceed vessel values by 10-50x
ROI protection: Insurance claims can preserve investment returns when accidents occur
Key Takeaway: The cost of comprehensive maritime insurance is a fraction of potential losses, making it essential for protecting maritime investment returns.
Modern Maritime Investment & Insurance: The Digital Asset Connection
The emergence of fractional maritime ownership through tokenization creates new insurance considerations that benefit modern shipowners.
Traditional Insurance in Digital Frameworks
Tokenized maritime assets inherit the same insurance protections as traditional ownership:
P&I coverage follows the vessel: Insurance attaches to the physical asset, not the ownership structure
Claims distribution: Insurance proceeds are distributed proportionally to token holders
Coverage verification: Blockchain records can provide transparent proof of insurance coverage
Enhanced Due Diligence Through Insurance Records
For fractional owners, insurance records provide crucial transparency:
Claims history: Past insurance claims reveal vessel condition and operational risks
Coverage adequacy: Insurance limits indicate professional assessment of vessel value and risks
Premium trends: Rising premiums may signal increasing risk factors
Shipowner Protection Through SPV Structure
Shipfinex’s Special Purpose Vehicle (SPV) structure provides additional insurance benefits:
Isolated liability: Each vessel’s insurance coverage is ring-fenced within its SPV
Professional management: Experienced operators ensure appropriate coverage levels
Regulatory compliance: Professional insurance management meets international requirements
From the Helm - Insider’s View: “When we evaluate vessels for tokenization, insurance coverage and claims history are critical factors. A vessel with comprehensive P&I coverage and a clean claims history indicates professional management and reduced investment risk. This due diligence protects token holders and supports sustainable returns.”
The Economics: How Insurance Costs Affect Maritime Profitability
Understanding insurance economics helps shipowners evaluate maritime investment opportunities more effectively.
Premium Structure and Risk Factors
P&I Clubs announced rate increases averaging 7% for 2025, reflecting inflation and claims trends. Premium calculations consider:
Vessel type and age: Newer, well-maintained vessels typically pay lower premiums
Trade routes: High-risk areas (piracy zones, congested ports) increase costs
Operator experience: Established operators with good safety records receive discounts
Claims history: Previous claims affect future premium calculations
Impact on Charter Rates and Investment Returns
Insurance costs directly affect maritime profitability:
Operating expense: Insurance represents 2-4% of total vessel operating costs
Charter rate factors: Ship owners incorporate insurance costs into charter pricing
Investment returns: Lower insurance costs improve cash flow available for distribution
2026 Market Trends
P&I clubs are expected to raise rates by 5% amid rising claims, with combined ratios expected to range between 100% and 105%. This trend reflects:
Inflation in repair costs: Shipyard costs and spare parts prices continue rising
Regulatory changes: New environmental and safety regulations increase compliance costs
Emerging risks: Cyber threats and climate change create new coverage needs
Key Takeaway: While insurance costs are rising, they remain a small percentage of vessel values and operating costs, providing excellent value for comprehensive risk protection.
Future of Maritime Risk Management: Emerging Trends for 2026
The maritime insurance landscape continues evolving to address new risks and opportunities.
Climate Change Adaptation
Rising sea levels and extreme weather events are reshaping maritime risk:
Route changes: Traditional shipping lanes may become unviable
Port infrastructure: Coastal facilities face increasing climate risks
Seasonal patterns: Hurricane seasons and storm intensity affect insurance pricing
Green shipping: Environmental compliance creates new coverage needs
Technology-Driven Risk Assessment
Digital technologies are transforming how insurers assess and price maritime risks:
IoT monitoring: Real-time vessel condition monitoring improves risk assessment
Satellite tracking: Enhanced navigation and weather routing reduce accident rates
Predictive analytics: Machine learning helps identify potential problems before they occur
Automated reporting: Digital systems improve claims processing and fraud detection
ESG Compliance and Sustainability
Environmental, Social, and Governance (ESG) factors increasingly affect insurance:
Carbon footprint: Emissions regulations may affect coverage availability and pricing
Social responsibility: Crew welfare and labour standards influence risk assessment
Corporate governance: Professional management structures receive preferential treatment
Sustainable operations: Green shipping practices may qualify for premium discounts
Regulatory Evolution
International maritime regulations continue to develop:
IMO 2030 strategy: New safety and environmental requirements affect coverage needs
Port state control: Enhanced inspections increase detention risks and insurance claims
Cybersecurity regulations: New requirements for digital security in maritime operations
Supply chain security: Enhanced cargo security requirements affect liability coverage
Conclusion: Insurance as the Foundation of Maritime Investment Security
The maritime industry’s transformation from exclusive high-net-worth investments to accessible fractional ownership depends fundamentally on robust risk management through insurance. With P&I Clubs covering 90% of the world’s ocean-going tonnage, the mutual insurance system provides a proven foundation for protecting maritime investments.
Key Takeaways:
Comprehensive protection: Modern maritime insurance covers operational, environmental, and financial risks that could threaten investment returns
Cost-effective risk management: Insurance premiums of 0.15-0.50% of vessel value protect against potentially catastrophic losses
Proven stability: The mutual P&I Club system has provided reliable coverage for over a century
Digital asset compatibility: Traditional maritime insurance seamlessly protects tokenised vessel ownership
Professional oversight: Experienced operators ensure appropriate coverage levels for fractional owners
For maritime shipowners, understanding insurance coverage isn’t just about risk management—it’s about recognizing the professional infrastructure that makes maritime investment viable. When evaluating fractional ownership opportunities, comprehensive insurance coverage signals professional management and institutional-quality risk management.
The maritime insurance ecosystem transforms the ocean’s unpredictable risks into manageable business expenses, creating the stable foundation necessary for maritime investment. In a world where a single container ship can carry $1 billion in cargo across oceans worth protecting, robust insurance coverage isn’t optional—it’s the bedrock of maritime commerce and investment security.
Disclaimer:
This material is provided for informational purposes only and does not constitute financial, investment, or legal advice. All digital assets carry inherent risks, including potential loss of capital. Past performance is not indicative of future results. Please review the relevant offer and risk disclosures carefully before making any financial decision.


